
Introduction to Types of Robot Wheels
Pardis Yavari2024-02-19T11:25:55+00:00For many years, robot wheels have evolved to be more efficient, satisfy specific requirements and be used in more complex machines which require moving in different settings. as a robotic enthusiast, you need to know how many robot wheels are out there and how they work. So you can have a better understanding of wheels’ application and make smarter choices when it comes to choosing wheels for your project.
Here in this article, we have gathered everything you need to know about the most well-known robot wheels.
Mecanum wheels
One of the strongest robot wheels that are commonly used in industrial machines and different robots is Mecanum wheels which Bengt Erland ILon created and patented in the 1970s.
A Mecanum wheel is a wheel with a series of rubber rollers placed on its circumference. These rubber rollers are located at 45 degrees. the rollers are diagonally mounted on the main part of the wheel at 45 degrees to the main axis. Unlike normal wheels which the driving force is applied in a straight line, the driving force in these wheels is applied at 45 degrees to the vehicle while the wheels move in a straight line. This position is the opposite of the rollers’ position in Omni wheels, which are perpendicular (90 degrees) to the body of the wheel.
As you see in the picture below, diagonally opposing rollers’ wheels have the same directions and but the rollers in the other two have different directions.
Now let’s take a look at how this wheel moves in different directions:
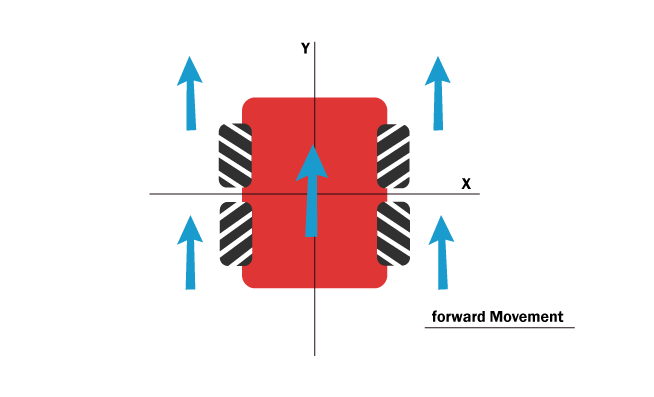
- Forward and backward
When a four-wheel vehicle (in this case a robot) wants to move forward and backward, the Mecanums act like regular wheels. Their rollers move forward or backward to move the vehicle.
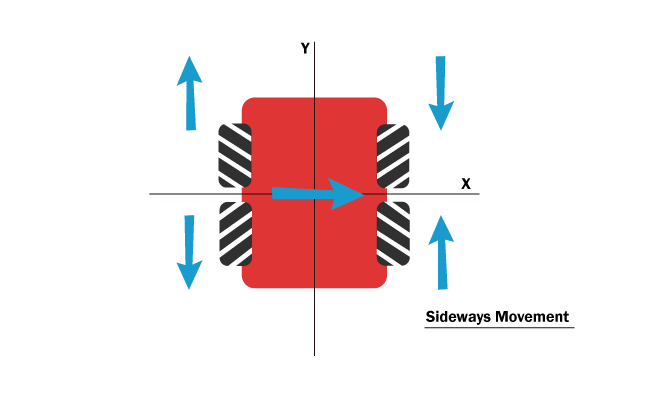
- Sideways movement
What happens when our four-wheel vehicle wants to move to the sides? In this case, as you see in the picture the two diagonally opposite Mecanum wheels move in one direction and the other two in the opposite direction. One of two the diagonally opposite wheels applies force to the vehicle, and the other one applies the driving force to the outside of the vehicle. The result will be a 180 degrees turn or side ward movement.
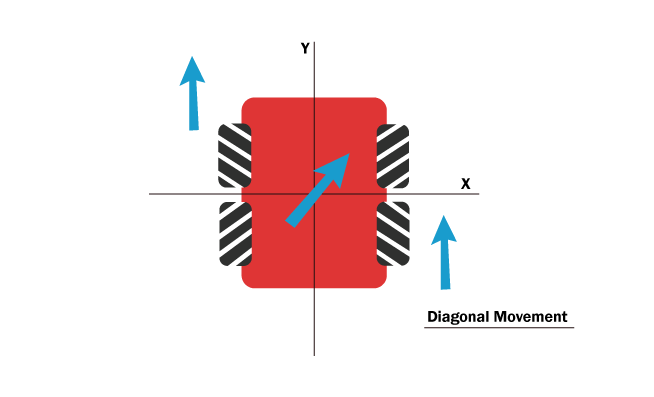
- Diagonal movement
To move our four-wheel vehicle diagonally, only one of the two diagonally opposite wheels needs to move. As you see in the picture below, our vehicle moves diagonally with the help of only two wheels.
Omni Wheels

Omni-directional wheel is also a multi-directional robot wheel like Mecanum wheels. They have rubber rollers that are attached around the main wheel to provide all sides movement. These rollers may vary in size. Some of them are small and used in plenty in just one wheel, while others are huge and stretched around the wheel. These rollers are like smaller wheels on top of the main wheel. Due to their position which is perpendicular to the main wheel, they can provide all direction maneuvers.
In terms of price, Omni wheels are more affordable comparing to mecanum wheels. so if it’s possible, choose Omni wheels to save some money. but if you can’t, go for mechanum wheels. At the end of the day, choosing robot wheels comes down to your project requirements and how much you can spend on robot parts.
You can read more on this topic in:
Caster Wheels

Caster wheels are non-powered wheels used to provide extra contact points and keep your vehicle stable and enable them to turn around. Most of them usually contain a fixed wheel secured inside a bracket and some of them have a frame and a ball inside it which are called ball casters. These wheels are idle wheels which means they are not fixed on an axle and no power is applied to them directly by motors, so they can turn around freely by an external force. to understand this better, imagine you’re in a grocery store. When you push a shopping cart to move, you’re the external power forcing the casters to move in any direction you want. The wheels will not move without you pushing.
Based on the setting, caster wheels can have different sizes, materials, and, shapes. For example, in an industrial environment, a machine or equipment with caster wheels needs to be able to move smoothly and also withstand heavy loads, while a shopping cart might not need high-performance caster wheels due to its application.
Fixed wheels

Fixed wheels are another type of tired robot wheels used in robots, vehicles, and equipment. As the name suggests, they are fixed in a position. They cannot rotate or turn to the sides without moving first. they usually contain a rubber tire that creates friction with the ground and a plastic or metal body.
Takeaways
As mentioned, the world of robotics and robot parts is developing real fast to make robot creation easier and more efficient and you as someone who passionately wants to create robots, need to know more about these wheels and their working principle. as you know now, there are 4 types of robot wheels:
- Mecanum wheels
- Omni wheels
- Caster wheels
- Fixed wheels
Find the best Robot Wheels on our Shop
Search our collection of robot wheels and buy robot wheels on our shop at the best price.


Leave a Reply