A Brief Guide to Holonomic Drivetrains
Pardis Yavari2024-04-09T07:17:38+00:00A holonomic drivetrain is a standard drivetrain used in many robotic competitions. Freedom of movement and agility are the two main factors in making it suitable for many conditions. The holonomic drive is an Omni-directional system, providing 360 degrees of maneuverability with the help of Omni wheels. This drive base can move to the sides effortlessly without turning the wheels. an exmple of a non-holonomic drivetrain is a car. The drive base of a car is not holonomic; as a result, it cannot move to the sides without turning the wheels. It can only move forward and backward or turn slightly to the left or right.
Holonomic Drive Types
There are different types of holonomic drivetrains:
- X-drive
- Kiwi drive
- H-drive
- Mecanum drivetrain
Each drivetrain has advantages and disadvantages you should be aware of before choosing. In this guide, We’ll walk you through critical things you need to know about them.
X-Drive
X-drive is a four-wheel Omni-wheel drivetrain that moves in any direction quickly. They can go straight and turn around in the blink of an eye. In this drivetrain, the wheels need to be placed diagonally at 45 degrees, and each of them need a separate motor. To understand better, look at the picture below:
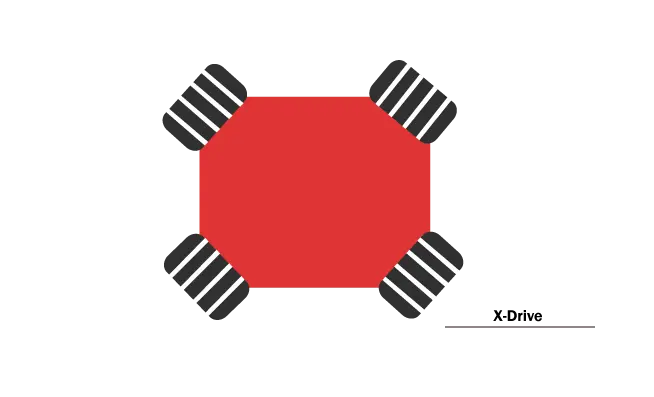
In the x-drive, the diagonally opposing wheels are in front of each other, creating an x frame. For a robot to move straight, one pair of opposing wheels moves forward, and the other stays idle. To spin the drive system in place, all wheels should move in one direction.
Kiwi-Drive
Another Omni-drive base or holonomic drive can be designed with three Omni wheels angled at 120 degrees. This drivetrain is known as Kiwi Drive or Killough Drive.

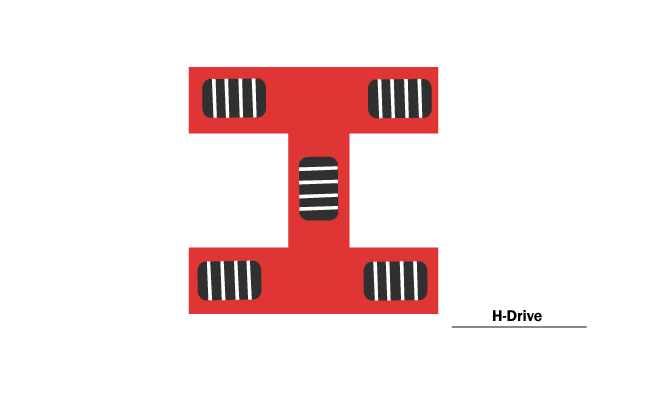
H-Drive
H-drive is an Omni-directional drive base with at least five wheels. Four wheels are installed like regular wheels pointing forward, and the remainder wheel is located at the center of the base perpendicular to the other wheels. The central wheel is responsible for strapping the whole robot to the sides. This drive base needs five motors for each of the wheels.
The h-drive is slower than the x-drive because it has an extra motor adding to the drive weight.
Mecanum Drive
Mecanum drive is also another holonomic drivetrains which can move in any direction utilizing mecanum wheels. Mecanum drives usually have four wheels facing forward. the wheels have rollers located at 45 degrees. It means when they start to roll, the force will be applied at 45 degrees to the robot. To move forward and backward, all wheels run in one direction. But to move the robot the sides, the diagonally opposing wheels turn in one direction and the other two moves to the opposing direction. These opposing forces cancels out each other, enabling the robot to move to the sides. the drive base can also move diagonally by only turning one of the two opposing wheels.
Mecanum drive are faster than h-drive but slower than x-drive in terms of forward and strafe speed.
Wrap up
Holonomic drivetrains are wonderful choices for many robotic competitions due to the acceleration and flexibility they offer. Each of them has its own strengths and weaknesses that you need to be aware of. To choose one of them, you need to consider the competition you are participating in and the most important factors that can make you successful.



Leave a Reply